Financial institutions face an ever-growing number of cyber threats, making it crucial to implement robust cybersecurity frameworks to prevent data breaches and ensure compliance with industry regulations.
This article will explore the best cybersecurity frameworks for financial institutions, each offering unique benefits tailored to specific needs and priorities.
On This Page:
- Introduction to Cybersecurity Frameworks
- NIST CSF: Best for Flexibility
- SOX: Best for Fraud Prevention
- GLBA: Best for Client Data Protection
- PCI DSS: Best for Credit Card Transaction Security
- FINRA: Best for Securities Industry
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022: Best Global Standard
- CIS Critical Security Controls: Best for Quick Data Protection
- C2M2: Best for Cybersecurity Maturity Evaluation
- NIST SP 800-53: Best for Federal Organizations
- Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Framework
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to Cybersecurity Frameworks

A cybersecurity framework provides guidelines and best practices aimed at aiding companies in their cybersecurity risk management. It also assists in meeting regulatory requirements. Financial institutions, in particular, need to have strong security controls in place to protect their critical assets, such as customer data, and maintain a strong security posture.
Some of the most widely-used cybersecurity frameworks for financial institutions include:
- NIST CSF
- SOX
- GLBA
- PCI DSS
- FINRA
- ISO/IEC 27002:2022
- CIS Critical Security Controls
- C2M2
- NIST SP 800-53
These frameworks offer a range of security controls and guidelines designed to address the unique challenges financial organizations face in managing cybersecurity risks and complying with industry regulations.
NIST CSF: Best for Flexibility
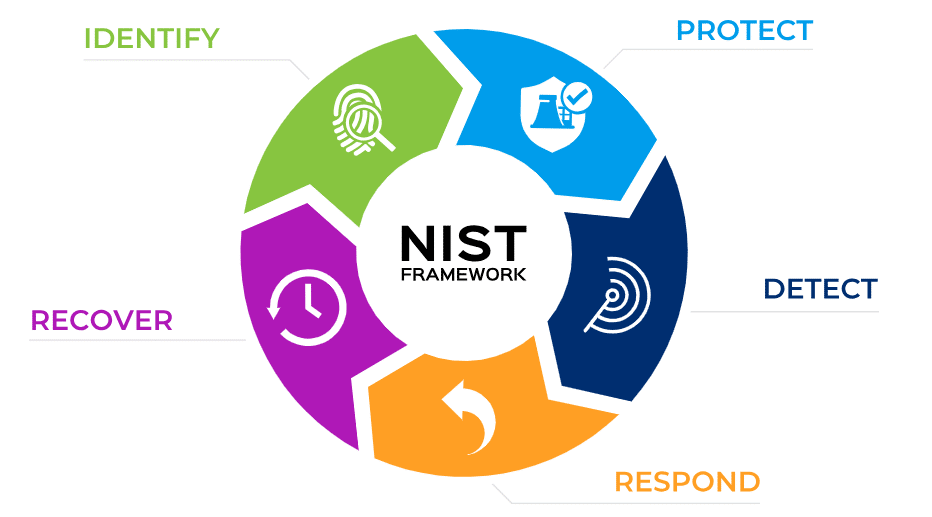
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a performance-based tool designed to help organizations assess their cybersecurity posture and identify areas for improvement. Its flexible and outcome-based approach makes it suitable for businesses of all shapes and sizes, including those in the financial sector.
Focusing on five crucial elements – Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover – the NIST CSF provides a strategic perspective on an organization’s management of cybersecurity risks.
- Identify helps organizations understand how to manage cybersecurity risk.
- Protect outlines safeguards to ensure critical infrastructure services.
- Detect defines activities to identify a cybersecurity event.
- Respond includes activities to react to a detected cybersecurity incident.
- Recover identifies activities to maintain resilience and restore any impaired capabilities or services due to a cybersecurity incident.
A key advantage of the NIST CSF lies in its adaptability, with the ability to tailor it to an organization’s specific needs. This flexibility allows financial organizations to focus on the most critical aspects of their cybersecurity program, ensuring that their systems and sensitive data remain secure while also complying with industry cybersecurity regulations. However, it’s worth noting that NIST CSF compliance is voluntary for private companies not under a government contract.
NIST is currently working on an updated version of this framework called NIST 2.0. This new version is expected to provide even more comprehensive guidelines and best practices for organizations to follow.
SOX: Best for Fraud Prevention
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (SOX) is a US statute that aims to prevent fraudulent transactions in the financial industry. SOX requires all financial reports to include an Internal Controls Report, which accurately represents a company’s financial facts.
Failing to comply with SOX can result in severe consequences, such as being taken off the public stock exchange, losing directors and officers’ liability insurance, or having directors removed.
In addition to its focus on financial reporting, SOX also provides guidance on storing financial information and covers typical cybersecurity threats, such as phishing attempts. Financial firms with a focus on fraud prevention would find implementing the SOX framework beneficial, as it aids in maintaining the integrity of their financial data and transactions.
GLBA: Best for Client Data Protection

The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) is a US statute that requires financial institutions to protect consumer data and inform their clients about how their data is being shared. Under GLBA, financial institutions must establish security controls to safeguard client information and maintain a strong security posture.
Failing to comply with GLBA can result in penalties, fines, and even jail time. As client data protection is a top priority for financial organizations, implementing the GLBA framework can help ensure the security of sensitive customer information and reduce the risk of data breaches.
PCI DSS: Best for Credit Card Transaction Security
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is designed to safeguard credit card transactions. This set of guidelines seeks to create a secure environment for all payments. Compliance with PCI DSS is mandatory for any company that processes credit card information, regardless of their industry.
Implementing the PCI DSS framework can be highly advantageous for financial institutions in the banking sector dealing with credit card transactions. By adhering to its comprehensive security controls, these institutions can protect sensitive payment card data and provide a secure environment for their customers to complete transactions.
Additionally, complying with PCI DSS can help financial organizations avoid hefty fines and penalties associated with non-compliance.
FINRA: Best for Securities Industry
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) is a self-regulatory organization that oversees financial firms in the securities industry in the US. FINRA requires firms to adhere to specific rules and cybersecurity regulations to protect customer data and prevent cyber threats.
Financial institutions operating in the securities industry can benefit from implementing the FINRA framework, as it provides a robust set of guidelines tailored to their specific needs in financial services.
ISO/IEC 27002:2022: Best Global Standard
The ISO/IEC 27002:2022 framework is a globally recognized standard for information security management, offering a comprehensive set of cybersecurity standards for financial organizations. By implementing the ISO/IEC 27002:2022 framework, financial institutions can demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive data.
While ISO/IEC 27002:2022 certification is not mandatory for most financial institutions, following the framework’s guidelines can help strengthen their security controls and ensure the protection of their critical assets.
Additionally, implementing an ISO/IEC 27002:2022 compliant Information Security Management System (ISMS) can help financial institutions meet other regulatory requirements, such as GDPR compliance.
CIS Critical Security Controls: Best for Quick Data Protection
The CIS Critical Security Controls, formerly known as the SANS Critical Security Controls, are a set of prioritized actions designed to help organizations protect against common attack vectors.
The framework offers high-priority and highly effective recommendations for rapid data protection, making it an excellent choice for financial institutions looking to secure their systems quickly.
Implementing CIS Critical Security Controls enables financial institutions to promptly tackle potential security risks and bolster their defenses against cyberattacks.
C2M2: Best for Cybersecurity Maturity Evaluation
The C2M2 (Cybersecurity Capability Maturity Model) framework is designed to help organizations assess their cybersecurity postures and maturity levels, enabling them to:
- Optimize their investments in cyber defense systems and procedures
- Evaluate their cybersecurity maturity
- Pinpoint areas for improvement
- Establish target maturity levels
- Prioritize actions to reach their goals promptly and efficiently
Using the C2M2 framework, financial institutions can:
- Gain valuable insights into their cybersecurity program’s effectiveness
- Identify areas for improvement
- Make informed decisions about allocating resources
NIST SP 800-53: Best for Federal Organizations
NIST SP 800-53 is an information security standard that provides a catalog of security and privacy controls for all U.S. federal organizations. Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the publication ensures that federal information systems and organizations are adequately protected.
Financial institutions that are also federal agencies can benefit from implementing NIST Special Publication 800-53, as it offers comprehensive security and privacy controls tailored to their specific requirements.
Choosing the Right Cybersecurity Framework

Selecting the right cybersecurity framework depends on the organization’s specific needs, priorities, and the industry regulations they must comply with. Factors to consider when choosing a framework include the types of services offered by the institution, the size of the organization, and any applicable industry cybersecurity regulations.
A careful assessment of their unique needs and priorities allows financial firms to choose the most fitting cybersecurity framework, fortifying their security posture, safeguarding customer data, and upholding industry regulations.
Implementing the right framework can help organizations mitigate cybersecurity risks, increase data security, and maintain a strong security posture in the face of ever-evolving cyber threats, including cyber-attacks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which cybersecurity framework should I use?
NIST Cybersecurity Framework is among the top choices when it comes to securing data, thanks to its comprehensive approach and robust policies. It is widely adopted and highly recommended for any organization. Furthermore, it’s worth noting that an updated version, NIST 2.0, is on the horizon, promising even more enhanced guidelines and best practices.
Who should use NIST Cybersecurity Framework?
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is a flexible framework that can be used by businesses of all sizes, sectors, and maturities to better understand, manage, and reduce their cybersecurity risk. It’s an excellent tool for everyone concerned or responsible for their own organization’s cybersecurity, as well as those in the energy and financial services.
What is the difference between NIST and Essential 8?
The Essential Eight is a set of eight security controls tailored for Australian organizations, while the NIST Cyber Security Framework is a comprehensive framework that maps to various regulatory standards and is designed to be applicable to organizations of any size and industry.
Are financial institutions required to comply with specific cybersecurity frameworks?
Yes, financial institutions are required to comply with specific cybersecurity frameworks, such as SOX and PCI DSS. NIST CSF is voluntary for private companies not under a government contract.



